(Good Regulatory practices)
Good Regulatory practices:
Introduction:
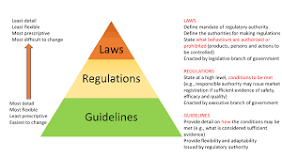
- Good Regulatory Practices (GRP) is processes, systems, tools, and methods for improving the quality of regulations that are internationally recognised.
- Before government initiatives are implemented, GRP systematically implements public consultation and stakeholder involvement, as well as impact analysis of government proposals to ensure they are fit for purpose and will achieve the goals set out.
Objectives:
- GRP provide a means of establishing sound and effective oversight of medical products as an important part of health system performance and sustainability.
- If consistently and effectively implemented, they can lead to higher quality regulation, improved regulatory decision-making and compliance, increased efficiency of regulatory systems, and better public health outcomes.
- They help to ensure that regulatory systems remain current as technologies and the systems in which they are used continue to evolve.
Community Pharmacy:
- In community pharmacy, GRP involves ensuring that all licenses and permits are up to date, and that all documentation related to drug dispensing, labeling, and storage is in compliance with local regulations.
- E-governance is used for managing drug dispensing records and renewals of prescriptions. Inspections are conducted regularly to ensure that the pharmacy is in compliance with regulatory standards.
Documentation for Hospital pharmacy License:
The documents essential for obtaining a sale license are:
- Constitution of the entity, Memorandum of Association (MOA), Articles of Association (AOA) for a company, partnership deed, LLP agreement in case of partnership and LLP.
- ID proof of partner/director/proprietor.
- Documents related to premises – Copy of ownership documents of property or rental agreement and NOC (No Objection Certificate) from the owner of the rented premises as the case may be.
- Site plan and key plan of the premises.
- Copy of Board resolution permitting obtaining of a license.
- Proof of availability of storage space as cold storage, refrigerator, etc.
- Copy of challan as proof of depositing fee.
- Affidavit regarding non-conviction of proprietor/partner/director and the firm.
- The affidavit from the registered pharmacist/competent person.
- Cover letter with name and designation of the applicant.
- Declaration form in a prescribed format.
- Applicant’s qualification certificate
For a pharmacist at a retail sale:
- Proof of qualification.
- Registration of local pharmacy council.
- Appointment letter
For a pharmacist at a wholesale sale:
- Proof of qualification.
- Experience certificate.
- Appointment letter
Prerequisites for Obtaining a License :
- Pharmacist/ Competent Individual: The pharmacist must be qualified in the case of a retail business. In the case of a wholesale business, the individual must be a graduate with 1-year experience or an undergraduate with 4 years of experience.
- Space Requirement: The other important requirement is space, that is the area of the pharmacy/unit. For both wholesale and retail licenses the area of the pharmacy/unit should be 15 square meters. In the case of a retail and medical shop, it should be 10 square meters. The clear height of the sales premises shall be as per the guidelines laid down under the National Building Code of India, 2005.
- Storage Facility: The other important requirement is storage facility since some drugs require to be stored in low temperatures, refrigerators and air conditioners are a must.
- Technical Staff: The retail pharmacy staff must be experienced with in-depth knowledge. The staff of the wholesale pharmacy must be a graduate with a minimum of 1-year experience or an undergraduate having four years of experience.
Types of Drug License
Looking at the definition of “drug”, the pharmaceutical business in India requires the following types of licenses:
- Manufacturing License– License issued to a business that manufactures drugs inclusive of allopathic/homoeopathy medicines.
- Sale License – License issued for the sale of drugs. It has the following bifurcations: – Wholesale Drug License – Retail Drug License
- Wholesale License – A drug wholesaler must obtain a wholesale licence. Wholesale means the sale of the drug to a person/retailer to further sell it.
- Retail License – A retail license is required for the retail sale of drugs. A retail sale means the sale of drugs or cosmetics for the consumption of the end consumer. Retailers can sell it to a dispensary, hospital, educational, medical, or research institute. Retailers engaged in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, stand-alone pharmacists, ayurvedic shops, etc need this license.
- Loan License – License issued to a business that does not own the manufacturing unit but uses the manufacturing facilities of another licensee.
- Import License – License is issued to any dealer importing the products for the manufacturing of drugs or is engaged in the business of importing drugs in India.
- Multi-Drug License – License issued to businesses that own pharmacies in multiple states with the same name.
Renewal of license
- Renewal of Sale license should be made on the application form same as the form submitted during the grant of the new license along with the necessary fee.
- The Fee for the renewal of the license is same as the grant of license. The late fee for the renewal of the license is as follows that is applicable up to six months.
Late fee for Renewal (Per month)
- Rs. 500+500 Rs. 1000.00 Rs.
- Rs. 250+250 Rs 500..00
- Rs. 250.00
- Rs. 250.00
Documents Required for Renewal
a) Copy of last renewal.
b) Affidavit of Pharmacist and current rent agreement.
c) Address proof of the authorised proprietor/applicant.
d) Affidavit of the liable person for day-to-day working and for any violation of drug laws.
Import and Export of of Drugs and Medical Devices:
- GRP in import and export involves compliance with regulatory requirements for the import and export of drugs and medical devices.
- Licenses and permits must be obtained before importing or exporting, and documentation related to import/export procedures, customs clearance, and transportation must be maintained.
E-Governance of license:
- E-governance of license refers to the use of electronic systems and technologies to manage the process of issuing, renewing, and revoking licenses by government authorities. This approach replaces traditional paper-based systems with digital platforms that allow for more efficient, transparent, and secure processing of licenses.
- E-governance of license can benefit both the government and the public by reducing administrative costs, improving accuracy and consistency of license data, and increasing access to services. It also allows for greater automation and integration with other government systems, which can improve data sharing and decision-making.
- The process of e-governance of license typically involves the use of online portals, mobile apps, and other digital platforms to allow citizens and businesses to apply for and manage licenses. These platforms may incorporate features such as online payment, document uploading, and real-time status updates.
- Overall, e-governance of license is an important aspect of digital transformation in government, which aims to improve service delivery and make government operations more efficient and transparent.

Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts, please let me know